-
HVAC systems play an essential role in most of our daily lives. HVAC systems keep us cool in the summer heat and warm in the cold of winter, more comfortable environment to be at. We’re all familiar with the air conditioning units we see in our homes and offices, but on a very large scale, it becomes necessary to make the cooling process more cost-effective. This is where chillers become such an important part of an HVAC system. Large buildings such as manufacturing plants, high-rise office towers and shopping malls generate a lot of heat during daily operations and this heat must be removed to keep occupants comfortable and equipment operating safely. Now, it’s time to dive in and discover more about the world of chillers.
-
The Fundamentals of Chillers
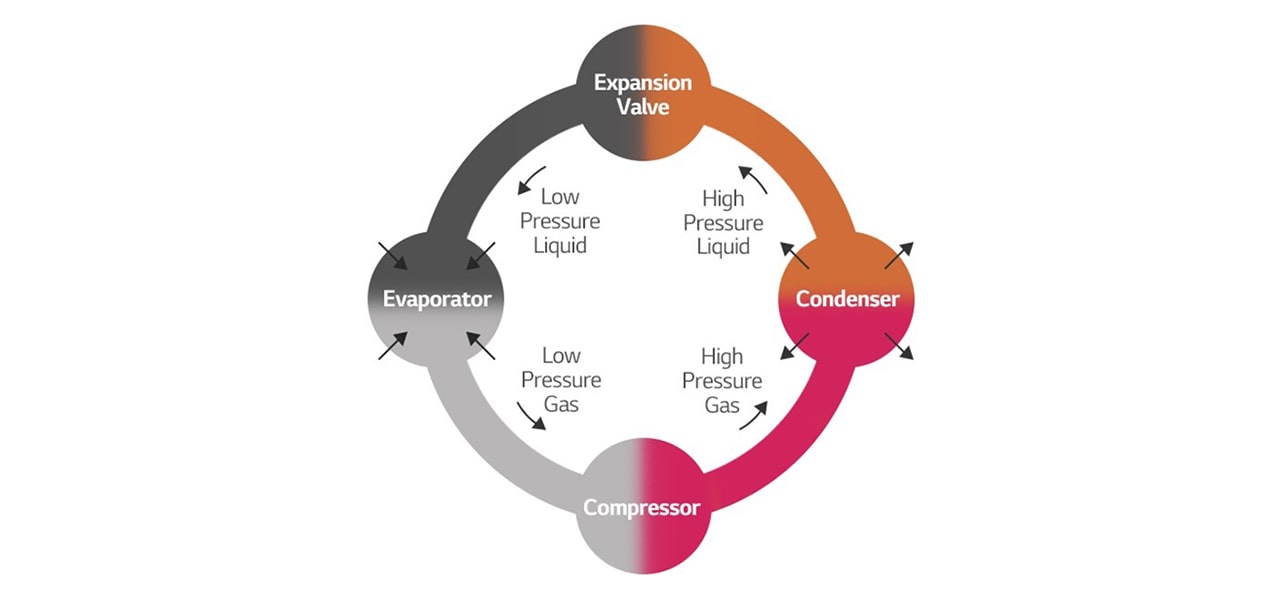
Much like the air conditioner in your home, chillers use refrigerant gas to move unnecessary heat between the evaporator and the condenser. This process chills the water and it is circulated throughout a building to draw in unwanted heat and remove it. This heat is then returned to the evaporator and the condenser then sends the heat to a cooling tower or cooling coil to remove the heat from the system. The procedure itself may sound simple, but these powerful machines are able to cool very large spaces and save a lot of money and resources in the process.

-
Types of Chillers
There are two types of chillers including air-cooled, water-cooled accordance with condenser type. What are the main differences between these chiller types? Let’s look at them now. The condenser in an air-cooled chiller is cooled by the ambient air in the environment. These systems are ideal for facilities with infrastructure and environmental restrictions or in locations where access to water is limited. They are also typically installed outdoors since they require access to the air in the environment. Water-cooled chillers are usually much larger than air-cooled chillers and their condensers are connected to a water tower for cooling. They are also more beneficial in facilities that require a constant high-performance operation. A water-cooled chiller can operate at high performance regardless of the ambient temperature as the temperature is regulated in the water tower and not affected by the outdoor environment.
And there is another type, called absorption chiller. absorption water chillers make use of the absorption refrigeration cycle and do not have a mechanical compressor involved in the refrigeration cycle. Absorption chillers utilize waste heat from other equipment and processes to chill water and provide cooling. With no compressor involved, these chillers can operate more cost-efficiently and with lower noise emissions. There are various types of chillers and each chiller type provides unique benefits for the installation environment.
-
Making the Right Choice When Selecting a Chiller
Now that we understand a bit more about the different types of chillers, how do you decide which chiller is best for a facility?
1. The first step is to determine the heat load of the facility to be sure the chiller has a large enough capacity to meet your needs.
2. Next, you should look at the target temperature required, the flow rate required and what type of refrigerant the system must use.
3. After you have determined these factors, you should look at the installation environment itself. Will the chiller need to be installed indoors or outdoors? Consider the performance of each chiller model based on capacity to be sure they meet the minimum chilled water supply temperature.
4. Then you need to look at the overall performance chiller pump to ensure it can meet requirements such as meeting the appropriate pressure to supply the necessary airflow.
The remaining factors to consider are also related to the install environment and include elements such as power supply, comprehensive control solutions, installation footprint, etc. You also need to be sure that the manufacturer is able to provide sufficient service in your region.
-
An LG Chiller for Every Customer
To meet the diverse needs of customers, LG offers chillers of various type, which is centrifugal chillers, screw chillers, scroll chillers and absorption chillers.

Centrifugal Chiller

Water-Cooled Screw Chiller

Air Cooled Screw Chiller

Air-Cooled Scroll Chiller

Absorption Chiller
-
Each customer has a unique set of needs and there is a chiller that can meet those needs. Understanding chillers better will help in the decision-making process and ensure you get the right chiller for your facility. Hopefully, you now have the power to choose the ideal chiller for whatever your needs may be.
Please click the 'INQUIRY TO BUY' banner below to contact your local LG office for further information on solutions and products.






