We use cookies, including cookies from third parties, to enhance your user experience and the effectiveness of our marketing activities. These cookies are performance, analytics and advertising cookies, please see our Privacy and Cookie policy for further information. If you agree to all of our cookies select “Accept all” or select “Cookie Settings” to see which cookies we use and choose which ones you would like to accept.
Finding Ways to Become an ESG Leader of Tomorrow
Environment, social and governance (ESG) considerations play increasingly crucial roles in a company’s prospects and viability. Key stakeholders, including consumers, investors, regulators and non-government organizations, are demanding that companies incorporate ESG factors into nearly every aspect of their business strategy and operations, from procurement and manufacturing through to product development and hiring.
As a global leader in information technology with 30 production sites worldwide, LG Electronics has recognized that for ESG management to be effective it needs to be integrated into a company’s day-to-day operations.
In 2018, the company outlined its strategic direction for ESG management based on standards required by the international community, which reflected the Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations. After reviewing its ESG performance over the previous three years, the company established a new direction for its ESG program and, in 2022, launched The Better Life Plan 2030.
The Better Life Plan 2030 includes six ESG commitments, three of which aim to significantly improve the company’s environmental performance by reducing its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and increasing the use of recycled materials in its products. For example, LG has committed to becoming carbon neutral by 2030 by reducing emissions generated from its production processes. To achieve this, the company plans to reduce by 50 percent the 1.93 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO2e) generated in 2017 by creating more energy-efficient facilities and adopting emission reduction technologies.
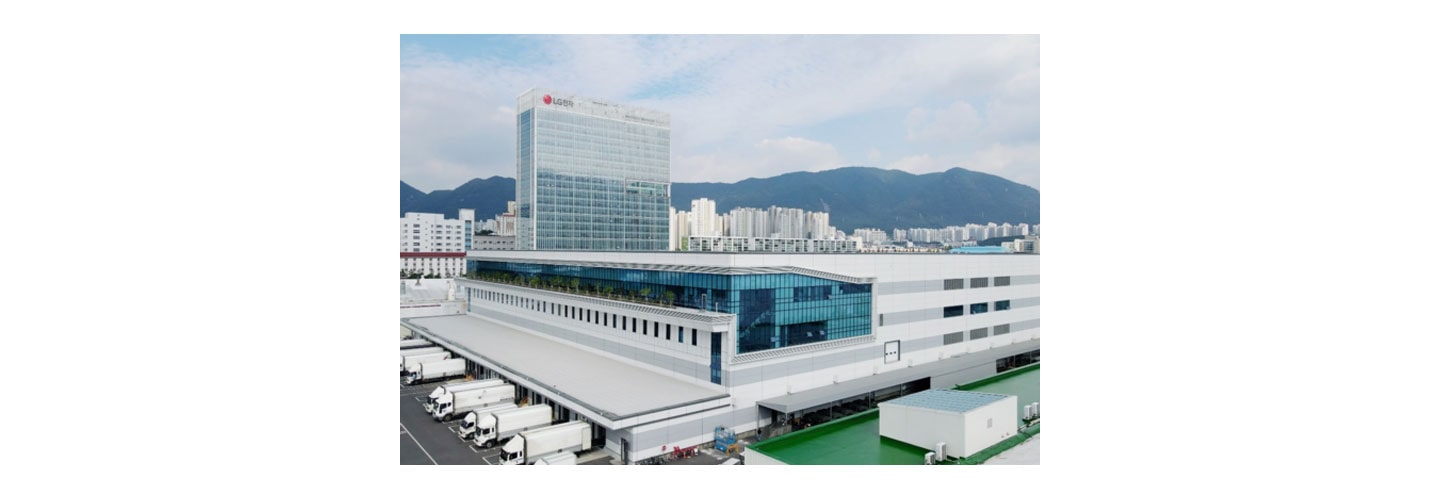

To support its carbon-neutrality goals, the company has transformed its factory complex, in Changwon, South Korea, into a futuristic manufacturing hub for its home appliances line. Renamed the LG Smart Park, the complex uses a digitally enabled 3D logistics system, advanced edge computing and machine learning analytics to predict defects, and state-of-the-art facilities to produce multiple models that respond to customer requirements.
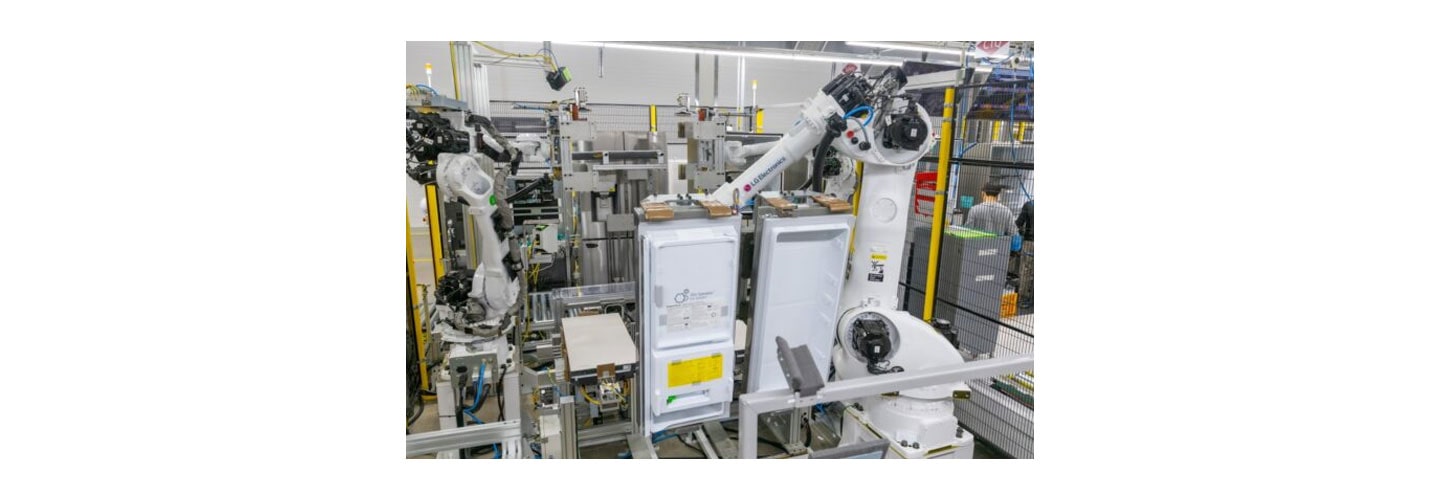

Earlier this year, the World Economic Forum (WEF) selected the complex as a Lighthouse Factory – these showcase companies that demonstrate leadership in using Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies. LG Smart Park has increased productivity by 17 percent and reduced the cost of defective-product returns by 70 percent. The factory has reduced GHG emissions and boosted energy efficiency per unit produced by 30 percent compared to an earlier site. The company plans to apply the smart production technologies pioneered at LG Smart Park to 26 of its production facilities in 30 countries, accelerating the digital transformation of its global manufacturing network by 2025.
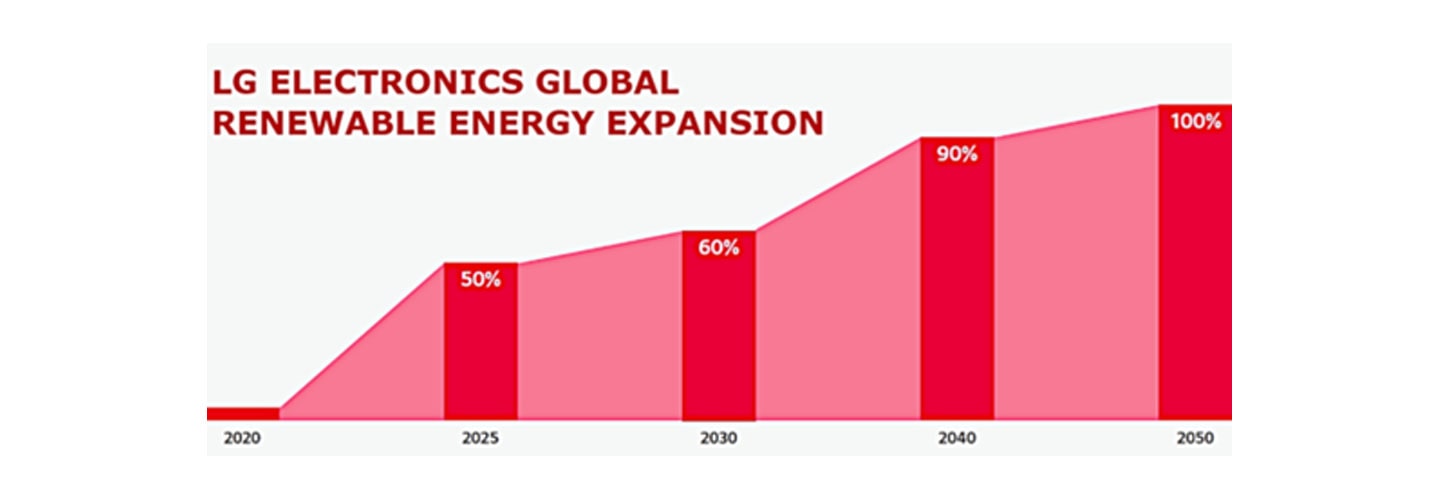
The remining 960,000 tCO2e generated in 2017 will be offset by securing carbon credits through the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change’s Clean Development Mechanism, which allows it to reduce emissions by investing in technology and capital in developing countries, and through external carbon reduction activities by utilizing its high-efficiency home appliances. And, under the ESG framework, the company aims to source 60 percent of its energy from renewable technologies by 2030, transitioning to 100 percent renewable energy by 2050.
LG is also committed to building a circular economy through waste recycling initiatives and improving waste treatment processes and aims to recycle 95 percent of waste generated at its global production sites by 2030, up from 92 percent in 2021, by utilizing 600,000 tons of recycled plastics in its manufacturing processes.
“Conducting product stability and quality reliability tests will improve resource efficiency, with recycled materials being used in a range of products, from washing machines and refrigerators to air conditioners and TVs,” say Hong Sung-min, head of LG’s ESG department. “LG is also implementing policies to comply with regional regulations on the take-back and disposal of e-waste by establishing infrastructure for the recovery of e-waste.”
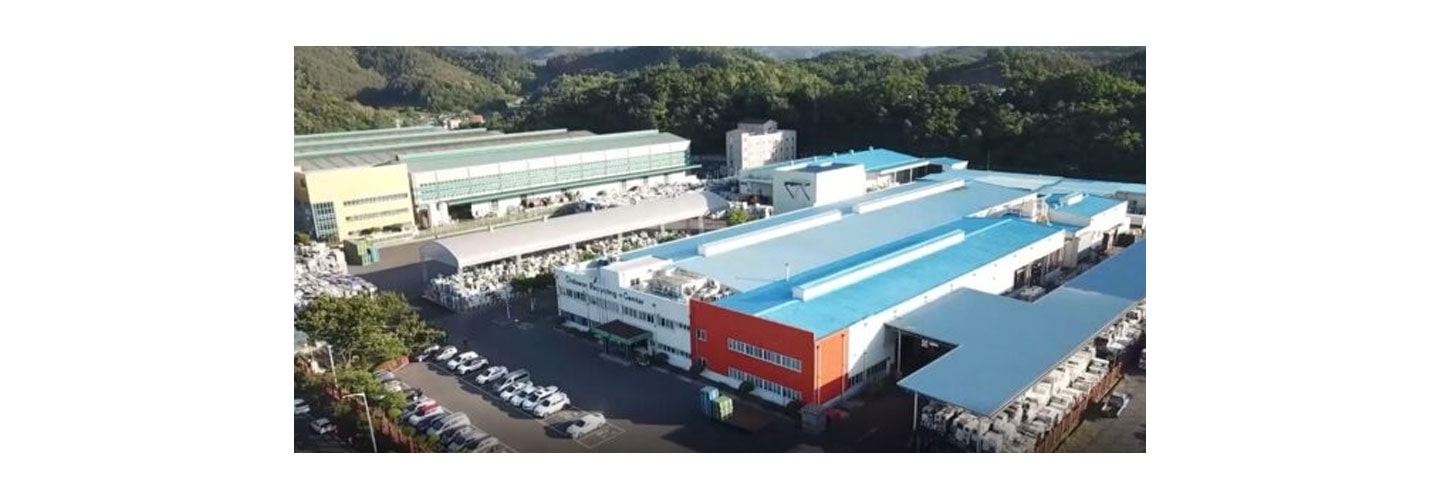

LG Chilseo Recycling Center
To support its efforts, the company opened the Chilseo Recyling Center, in South Korea, in August 2001. “The facility is spearheading the company’s e-waste initiative by collecting electronic waste at the end of product lifecycles and re-using recycled plastic to manufacture new components for use in home appliances like refrigerators,” adds Hong.

LG is also improving the energy performance of its products. Earlier this year, the company launched its new ThinQ washing machine, which features an Artificial Intelligent Direct Drive (AI DD) motor, which uses deep learning to identify different types of fabrics and then selects the optimal cycle and settings for each load. In a first for the home appliance industry, the AI technology applied to the upgradable appliance laundry solutions received the AI Algorithm Reproducibility Process Verification from UL, a global safety science leader, which helps companies to demonstrate safety, enhance sustainability and achieve regulatory compliance.
“LG’s current activities are in line with our mid- to long-term ESG strategy to produce eco-friendly products and services for future generations,” says William Cho, CEO of LG Electronics. “LG is actively working on environmental solutions, so that future generations can enjoy a better life and contribute to a better tomorrow.”
This story was edited from an editorial feature article published in Nature magazine.


