-
Chiller vs. VRF? Deciding which system type is best for your business can be quite a challenge. That’s why we took the opportunity to talk to an LG chiller specialist and an LG VRF specialist to hear what they had to say about which system is best for different environments. When it comes to factors such as facility size, investment, operation costs, and maintenance, each specialist has a different opinion. We take a deep dive into this topic with these LG specialists to help discover which type of system is best for a wide range of business types. Join us for this heated debate!


-
Q. Tell us a brief introduction to the advantages of chillers and VRF systems.
Seo: Depending on the type of compressor, chillers are divided into scroll, screw and centrifugal types. The biggest advantage for all chiller types is that they provided a large capacity for each individual chiller unit and deliver high efficiency.
Lee: The target temperature for each space in a building may be different. I feel that the biggest competitive edge for a VRF system is that it can control the temperature for each individual space.
Lee: I think it’s important to first assess the purpose of each space in a facility before proposing an HVAC solution to the customer. It’s advantageous to implement VRF systems in small to medium-sized buildings that have unique uses for each floor and space in the building with different usage times. Some examples of these types of facilities are small to medium-sized shopping centers, office spaces with multiple companies, shopping malls, movie theaters, small hospitals with operating rooms, treatment rooms, and patient rooms, as well as commercial rental buildings and hotels.
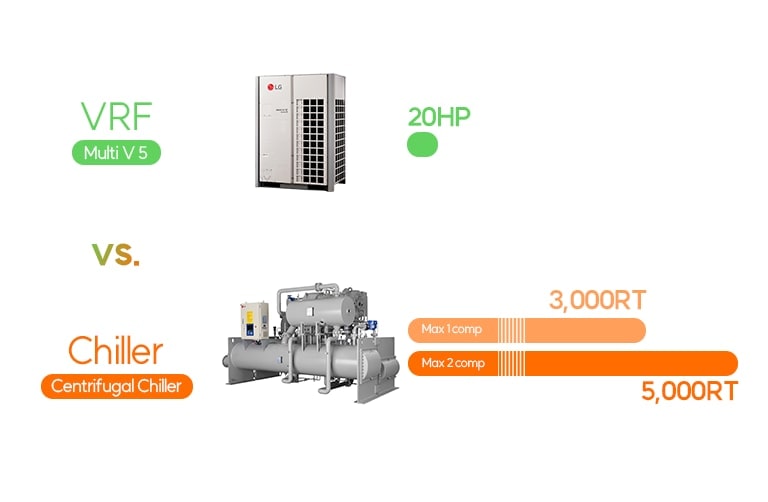
Seo: It is difficult to say which system is more advantageous because it depends many factors such as the region of the installation, but I think that a chiller is more suitable for a 500RT scale system.
When it comes to chillers, because the capacity that can be covered by a single unit is larger than a VRF, chillers are more advantageous for larger facilities. Additionally, chillers are better for high-rise buildings because there less of a restriction on the length of piping than there is with VRF systems. Also, chillers are water-cooled systems and their efficiency is much higher than that of a VRF, making them even more suitable for large-scale facilities because they consume more energy overall.

-
Q. Which system type is more efficient in terms of both initial investment and operating costs?
Lee: When you compare only the cost of the product equipment, the initial investment is actually similar. However, because a VRF system does not require 3rd-party equipment installation costs. including water piping and automated control systems, the initial investment is relatively low.
I also think VRF is more competitive when it comes to operating costs. If you compare the operating costs of an air-cooled VRF and a water-cooled chiller, the two system types are similar. The chiller system may even perform better when it comes to costs depending on the season. However, a VRF may be more beneficial when you factor in the operating costs of the air conditioning equipment connected to the chiller as well as 3rd-party equipment such as pumps, cooling towers and FCUs.
Of course, when it comes to a water-cooled VRF system, additional costs 3rd-party equipment such as a chiller must also be taken into account. However, even in this scenario, a water-cooled VRF system can save energy by being designed to manage refrigerant flow rates and variable flow rates to control indoor units individually or implement 3rd-party systems to control pumps and water flow. Therefore, actual operation costs for water-cooled VRF systems can be considered to be lower than chillers.
Seo: Initial investment for a water-cooled chiller system is higher than a VRF system because additional equipment is required such as cooling towers, pumps and air handlers. However, the efficiency of a water-cooled chiller can be up to twice as good as an air-cooled VRF or chiller, and it can be used for a wider range of applications. Although some may argue that cooling towers and pumps also consume energy, I think these costs are insignificant when compared to the operating costs of the chiller system overall.
In the HVAC market, not only do we need to consider operating costs, but we must also take other factors such as comfort, efficiency, manageability, convenience, and maintaining existing processes into consideration. So, I think that chillers and VRF systems are competitive in projects up to 500RT in scale. I’m responsible for the Latin American market and in this region, chillers are more commonly chosen for projects 500RT or larger due to the consideration of installation, operating costs, and other factors.
-
Q. Is maintenance more convenient for chillers or VRF systems?
Seo: People often say that the convenience of maintenance depends of the structural characteristics of a system, but this really depends on which solution is used more commonly in a region.
For example, in the Panamanian and Columbian markets in Latin America, there is a lot of influence from the US and locals are more familiar with chiller systems. Consultants in the region are more familiar with water pipe system design and local installer are better equipped to perform maintenance on chiller systems.
Although the preferred system type may differ for each country, the North American and Latin American markets tend to favor chillers. The chiller market is much more dominant in the Middle East (UAE, Saudi Arabia) as well. In Asian markets, chillers are widely implemented in large shopping malls, hotels, and industrial facilities. In these locations, chillers offer advantages when it comes to maintenance.
Lee: Building administrators seem to prefer VRF systems. When it comes to maintenance alone, VRF systems less expensive and easier to maintain than chillers. Typically, building administrators are more concerned with the all equipment related to heating and cooling, not just the chiller or VRF equipment itself. VRF systems are comprised of just outdoor units, indoor units, refrigerant piping, and control systems. I think building administrators prefer VRF systems because there are fewer points to consider for maintenance than chillers.
Also, VRF systems have an advantage of having maintenance performed by a single brand. Conversely, a chiller may require the administrator to manage all the different brands of the various equipment or they may need to hire a maintenance company to manage all of these elements.


-
Q. Which system type is more eco conscious?
Seo: There are a few factors that make chillers more eco conscious.
1. In the case of water pipe systems (chillers), they can be a bit more eco conscious because they use water to cool the air instead of refrigerant. Of course, chillers do use some refrigerants, but this usage is limited to certain refrigerant cycle configurations.
2. Additionally, the efficiency of a water-cooled system is much better than an air-cooled system (VRF).
3. Finally, absorption chiller system that utilize waste heat sources for heating and cooling are officially recognized as eco conscious solutions in many regions and also make users eligible for tax benefit.
Lee: I think VRF systems are more eco-conscious. Because VRF systems can use natural energy sources such as air or geothermal energy. In fact, in some European countries, some VRF systems are recognized as new and renewable energy solutions.


-
Q. Both chillers and VRF systems have their clear advantages. Are there any new solutions that highlight the strength of each system type?
Lee: Individual chiller units have a large capacity and these systems can be custom made with nearly no capacity limit, but these systems do have the disadvantage of being difficult to control individually. On the other hand, since the Multi V air-cooled VRF system is directly connected to the indoor units, it is possible to freely control the refrigerant flow rate, making individual control quite easy. But there are restrictions when constructing a large-capacity system. The disadvantage of VRF systems is the large amount of space required for installation in a large-capacity system.
In order to compensate for the shortcoming of each system type, the Multi V Water and air-cooled chiller systems were developed. The Multi V Water is water cooled but it uses the VRF refrigerant method that makes it easier to manage control for individual spaces, which is typically difficult for chiller systems. In addition, because it is a water-cooled heat exchange system that can be installed inside buildings, there are fewer limitations when it comes to installation space. An air-cooled chiller can also be constructed for a large-capacity system using an air heat exchange method. It is relatively easier to configure and operate the air conditioning system than with a water-cooled chiller system.
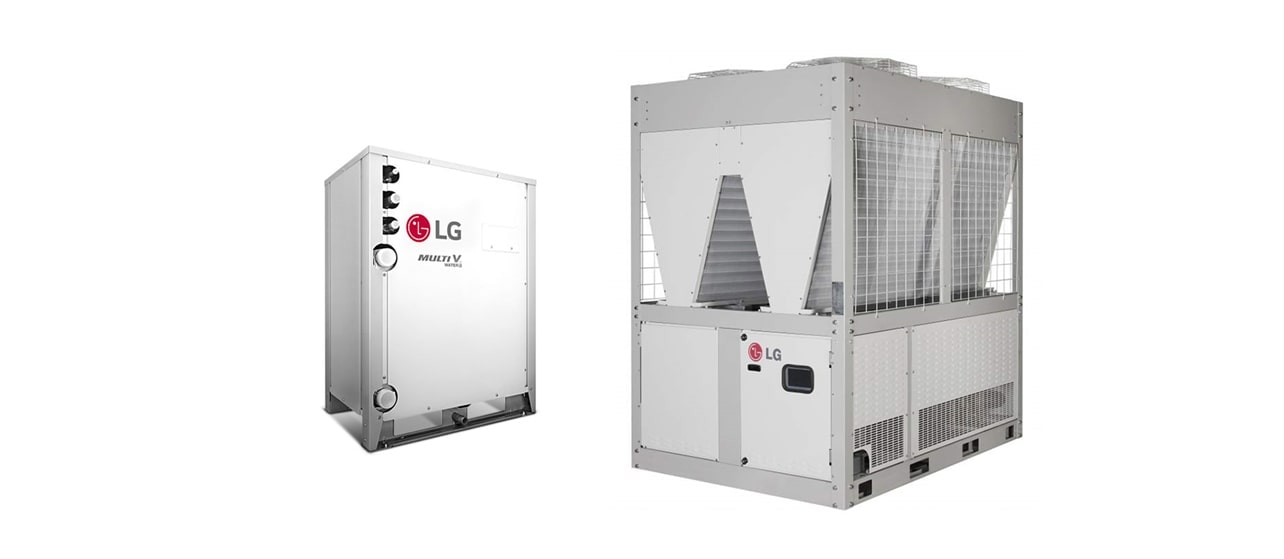
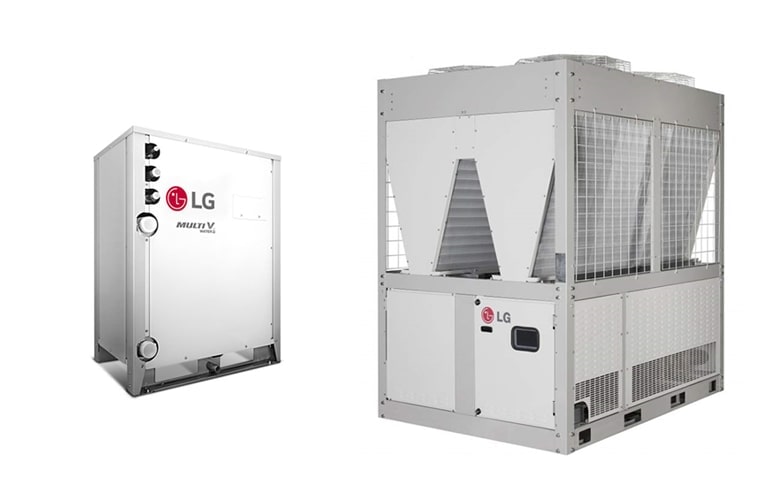


-
Q. By chance, are there cases when a chiller and VRF system are implemented together?
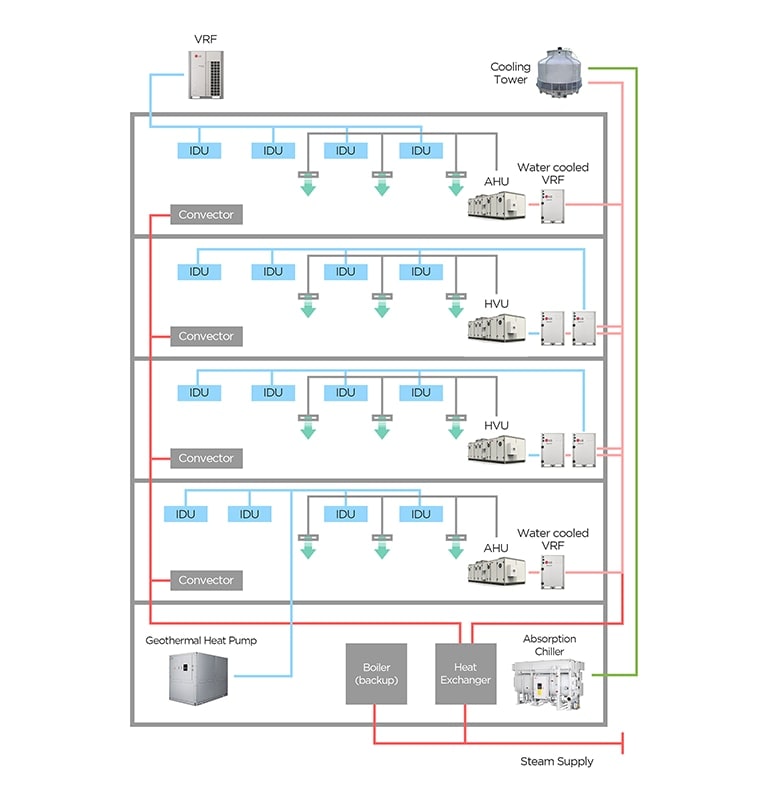
Seo: In facilities that are used for multiple purposes, chillers and VRFs can be used together. A chiller and VRF system can be configured together for almost any facility type, including hospitals, hotels, and industrial plants. It is recommended to use a chiller in areas that require large capacity cooling loads and to use VRF in common office spaces or areas that not require large capacity loads.
Actually, in a large-scale hospital in Costa Rica, a chiller was installed for an operating room when temperature and humidity must be kept constant, and VRF was installed for offices and meeting rooms.
Lee: In the office building where we work, the areas where our desks are located requires heating and cooling for 8 hours a day during working hours. However, the conference room only requires climate control when there are meetings. If both of these areas of served by only a chiller system, the conference room with be heated and cooled even when it is not needed and this will result in wasted energy consumption. For cases like this, energy can be saved by using a chiller for the office space and VRF for the conference room.
LG Science Park and the R&D center at Changwon Smart Park Factory 1 in Korea are examples of facilities that use hybrid systems with LG chillers and VRF systems together.

-
Q. Which market or facility type most commonly chooses chillers or VRF systems?
Seo: VRF is becoming popular in commercial and residential facilities but chillers are still much more common in large facilities such as airports, factories and large hotels. In buildings that require a large heat load, chiller products are more common.
Additionally, chillers are overwhelmingly preferred for factory processing applications.
It depends, but I think chillers are chosen for projects that require a capacity of 3-400RT or more.
Lee: VRF systems are the preferred solution for facilities with multiple purposes such as schools, markets, shopping malls, residences, offices, hospitals, and other commercial facilities. VRF systems are increasingly being implemented in facilities with applications that continue to expand such as modular buildings. Although VRF used to be the more popular choice for small buildings, it has recently become more popular in medium and large-scale buildings as well. In recent years, real customer needs such as air purification indoor units, airflow diversification, and hygiene technology for cleaner air, have been driving the development and growth of VRF applications.
Deciding between a chiller or VRF system is not an easy task. That’s why we looked to the specialist for expert advice and to hear both sides of the story. We hope this debate has helped you understand the technologies better and brought you closer to grasping what type of system would most benefit your facility.
-
We published second white paper 2022 about Chiller and VRF. For more detailed information on the chiller or VRF debate, download our white paper on this topic below. Our goal with this white paper is to address the benefits of each type of system and help people with their decisions-making process when planning for, and designing an apt HVAC system. If you want to download whitepaper, please click the button below.






